Quantum Computing
Quantum computing is a technique whereby quantum phenomena such as superposition and entanglement are used as the basis for performing computational tasks.

The fundamental building block of quantum computation systems is the qubit. Qubits are in some ways similar to, and different than, bits in conventional computers. Similar to conventional bits, qubits have two primary states, “0” and “1”. However, in conventional systems, the states are completely binary. In other words, the bit can only take on these two values.
However, a qubit can take on any number of intermediate states between “0” and “1”, along a three-dimensional space called a “Bloch sphere”. Furthermore, when additional qubits are combined together, the states can become “entangled”, and it is this entanglement that allows extremely complex operations to be performed with only a few qubits.
Bloch Sphere
Quantum computers are capable of solving many computational problems such as integer factorization much faster than conventional computers, and have the potential to solve future problems unattainable by current systems.
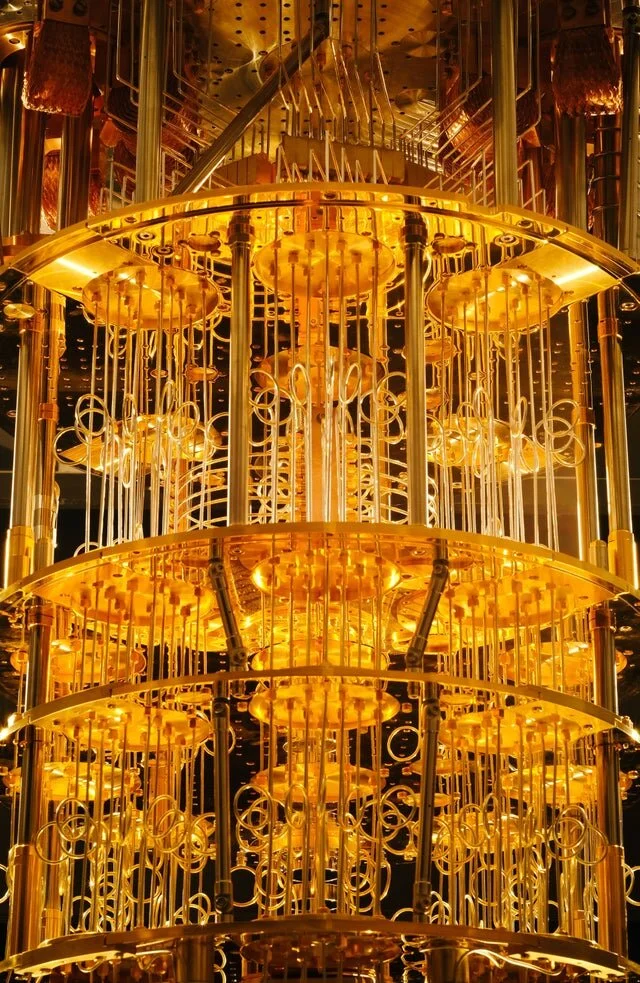
dilution refrigerator
Image by Graham Carlow, license
Quantum computing is currently in its infancy, with many substantial challenges that still need to be overcome. One of the most important is the issue of decoherence. Quantum computers can only solve problems precisely if quantum coherence can be maintained. This requires them to operate at cryogenic temperatures (typically a few 10’s of milliKelvin), and limits the number of qubit operations that can be performed.

Next Steps
There are many platforms for quantum computing currently being implemented and under investigation. These include ones based upon superconducting Josephson junctions, trapped ions, cold atoms, quantum dots, defects states and topological materials. All of these have advantages and disadvantages and it is unclear which ones, if any, will ultimately emerge as the most promising for large-scale implementation.